quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues|Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues : wholesaler Finite element (FE) modeling has greatly advanced the quantification of tissue stress and strain in biaxial tension and, by applying biaxial tests and FE models, within the .
WEBNotice communale. Informations sur la feuille Cassini. Légende de la carte Cassini. Cliquez sur un outil puis sur la carte. Vue générale. Zoom rectangle. Zoom progressif. Nom de la commune. Sélection rectangulaire.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Clientes Controle e Express, solicitem a ativação do seu Roa.
A technique for the quantification of the strain field in the central region of biaxially tested planar soft tissues is presented. A vidicon-based image analysis system interfaced to a PDP 11/34 minicomputer is employed to track particles affixed to the specimen surface in real-time, from .DOI: 10.1016/0021-9290(87)90267-3 Corpus ID: 30901141; Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues. @article{Humphrey1987QuantificationOS, title={Quantification of strains .Europe PMC is an archive of life sciences journal literature. Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues.
A custom-built versatile biaxial testing system handles a wide variety of soft biologcial tissues. Biaxial system employs a variety of gripping/clamping mechanisms, .
Soft tissue strain measurement
Humphrey, J.D., Vawter, D.L. and Vito, R.P. (1987) Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues. Journal of Biomechanics , 20 (1), 59–65. Article CAS Google Scholar Finite element (FE) modeling has greatly advanced the quantification of tissue stress and strain in biaxial tension and, by applying biaxial tests and FE models, within the .In this paper, we use a constrained mixture theory for growth and remodeling of planar soft tissues to motivate a new experimental approach for investigating competing hypotheses on, . Advancements in hierarchical strain analysis of tissues and reconstituted collagen constructs came with the integration of uniaxial and biaxial testing devices and various imaging modalities.
A technique for the quantification of the strain field in the central region of biaxially tested planar soft tissues is presented. A vidicon-based image analysis system interfaced to a PDP 11/34 . A technique for the quantification of the strain field in the central region of biaxially tested planar soft tissues is presented. A vidicon-based image analysis system interfaced to .
The measurement of strain in soft tissues has proven to be a difficult task. Thus many different techniques have been proposed, optical and otherwise. . R.P. (1987) Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues. Journal of Biomechanics, 20(1), .DOI: 10.1016/0021-9290(80)90165-7 Corpus ID: 20124342; The mechanical properties of soft tissues--I: a mechanical system for bi-axial testing. @article{Vito1980TheMP, title={The mechanical properties of soft tissues--I: a mechanical system for bi-axial testing.}, author={Raymond P. Vito}, journal={Journal of biomechanics}, year={1980}, volume={13 11}, .
Internal pressure in the healthy human annulus fibrosus leads to multiaxial stress in vivo, yet uniaxial tests have been used exclusively to characterize its in vitro mechanical response and to determine its elastic strain energy function (W). We expected that biaxial tension tests would provide unique and necessary data for characterizing the annular material response, and .In this study, digital image correlation (DIC) was adopted to examine the mechanical behavior of arterial tissue from bovine aorta. Rectangular sections comprised of the intimal and medial layers were excised from the descending aorta and loaded in displacement control uniaxial tension up to 40 percent elongation. Specimens of silicon rubber sheet were also prepared and served as a .
Abstract A technique for the quantification of the strain field in the central region of biaxially tested planar soft tissues is presented. A vidicon-based image analysis system interfaced to a PDP 11/34 minicomputer is employed to track particles affixed to the specimen surface in real-time, from which the strains are inferred.In particular, because stress and strain fields can be homogeneous in a central region of a biaxially tested tissue, and because biaxial testing admits diverse protocols wherein equal stresses can be imposed in the presence of unequal strains or stresses can be maintained in the absence of strain, we report simulations that illustrate the . The ability to synchronize motion and data capture with image capture for Digital Image Correlation (DIC) analysis: Studies wherein mechanical tests are performed on soft tissues do not generally employ strain gauges for strain measurement due to the difficulty in bonding such gauges to tissues and the large range of strains observed when .
A.H. Hoffman and P. Grigg, A method for measuring strains in soft tissue. J. Biomech. 10 (1984) 795–800. Article Google Scholar J. Humphrey, D. Vawter and R. Vito, Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues. J. Biomech. 20(1) (1987) 59–65. Article Google Scholar
We further showed that in-plane shear stresses definitely exist in biaxially tested human ventricular myocardium, but can be reduced to a minimum by preparing the specimens in an appropriate manner. The windows serve as a venue to acquire images that encompass the interfaces and enable quantification of the relative displacement between the prosthesis, cement, and bone that result from axial loading of the prosthesis. . “Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues,” J. Biomech. , 20 (1), 59 –65 (1987). Google Scholar . The integrated instrument is capable of a wide-field quantification of the fiber orientation and the degree of optical anisotropy (DOA), representing the local degree of fiber alignment. . Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues. J. Biomech. (1987) A. Anssari-Benam et al.
It is shown that in-plane shear stresses definitely exist in biaxially tested human ventricular myocardium, but can be reduced to a minimum by preparing the specimens in an appropriate manner, and whether shear pressures can be neglected when performing planar biaXial extension tests on fiber-reinforced materials. One goal of cardiac research is to perform . A technique for the quantification of the strain field in the central region of biaxially tested planar soft tissues is presented. A vidicon-based image analysis system interfaced to a PDP 11/34 .“Integration of polarized spatial frequency domain imaging (pSFDI) with a biaxial mechanical testing system for quantification of load-dependent collagen architecture in soft collagenous tissues”, Acta Biomaterialia . Vito R.P. Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues. J. Biomech. 1987; 20 (1):59–65. [Google .Europe PMC is an archive of life sciences journal literature. Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues.
A technique for the quantification of the strain field in the central region of biaxially tested planar soft tissues is presented. A vidicon-based image analysis system interfaced to a PDP 11/34 .
A.H. Hoffman and P. Grigg, A method for measuring strains in soft tissue. J. Biomech. 10 (1984) 795–800. Google Scholar J. Humphrey, D. Vawter and R. Vito, Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues. J. Biomech. 20(1) (1987) 59–65. Article Google Scholar
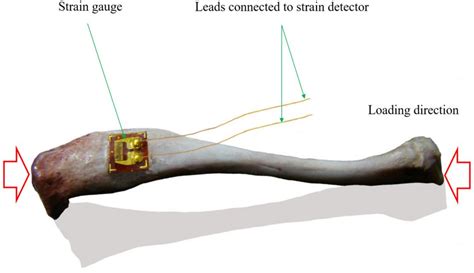
Bulge test, also known as the inflation test, is the most common type of biaxial test conducted on elastomers and thin films (Fig. 1 b).However, thickness variations throughout the membrane during pressurisation result in severe nonlinear mechanical behaviour i.e. inhomogeneous stress and strain distributions, in particular at large strain amplitudes so that . To design more effective tissue-engineered heart valve replacements, the replacement tissue may need to mimic the biaxial stress–strain behavior of native heart valve tissue. This study characterized the planar biaxial properties of tissue-engineered valve leaflets and native aortic valve leaflets. Fibrin-based valve equivalent (VE) and porcine aortic valve . In particular, because stress and strain fields can be homogeneous in a central region of a biaxially tested tissue, and because biaxial testing admits diverse protocols wherein equal stresses can be imposed in the presence of unequal strains or stresses can be maintained in the absence of strain, we report simulations that illustrate the .
scuff proof tester
3m scuff it
2.1. Foundational Studies. Sacks and Sun elegantly captured the history and evolution of biaxial testing in their 2003 review entitled “Multiaxial Mechanical Behavior of Biological Materials” [], with a special focus on the challenges related to the testing of biological soft tissue for the development of constitutive theories.This review serves as an excellent .To facilitate bioprosthetic heart valve design, especially in the use of novel antimineralization chemical technologies, a thorough understanding of the multiaxial mechanical properties of chemically treated bovine pericardium (BP) is needed. In this study, we utilized a small angle light scattering based tissue pre-sorting procedure to select BP specimens with a high degree .
scientific article published in January 1987. Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues Q50802511)
Quantification of Shear Stresses and Strains in the Human Myocardium 2335. shear stresses can be neglected when performing planar . and related stresses of several biaxially tested soft biological tissues. MATERIALS AND METHODS Material In this study, myocardial tissue specimens (n = 14) from the left ventricles of nine human hearts (mean age Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues J. Biomech. , 20 ( 1 ) ( 1987 ) , pp. 59 - 65 , 10.1016/0021-9290(87)90267-3 View PDF View article View in Scopus Google Scholar
Therefore to effectively model the mechanical response of transversely isotropic soft tissue, one must include both anisotropic invariants in the strain-energy function. 5. Non-linear deformations. Heretofore only the consequences for the infinitesimal strain regime of dependence on only one anisotropic invariant have been explored.This paper considers the problem of measuring the strain field in biaxially loaded elastic membranes, such as soft biological tissue. Cross-correlation of intrinsic or applied speckle patterns were used to calculate the 2D displacements of small regions on the surface of a deforming membrane. This m .
Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues.
Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues

Spela slots gratis på nätet (utan nedladdning). Spela mer än .
quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues|Quantification of strains in biaxially tested soft tissues